CryptographyUniversity of Maryland College Park This course is definitely one of the best that you shouldn’t miss out on. It is a wide-ranging course covering tons of topics, meanwhile many of them are taught in depth. I love the syllabus, the pace, and the internal logic among different modules. Learning this course is an amazing…
Category: Cryptography
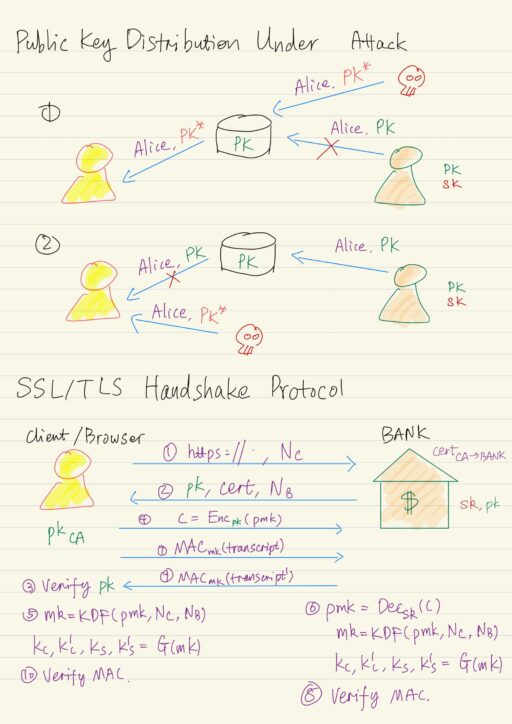
Public Key Infrastructures & SSL/TLS
An attacker can try to manipulate the public key distribution process. In particular nothing prevents an attacker from inserting attacker’s public key pk* into the public database but claiming other’s name in order to overwrite the original public key pk. Moreover, the attacker may prevent or block the communication from any party from reaching the…
Discrete Logarithm Based Digital Signature
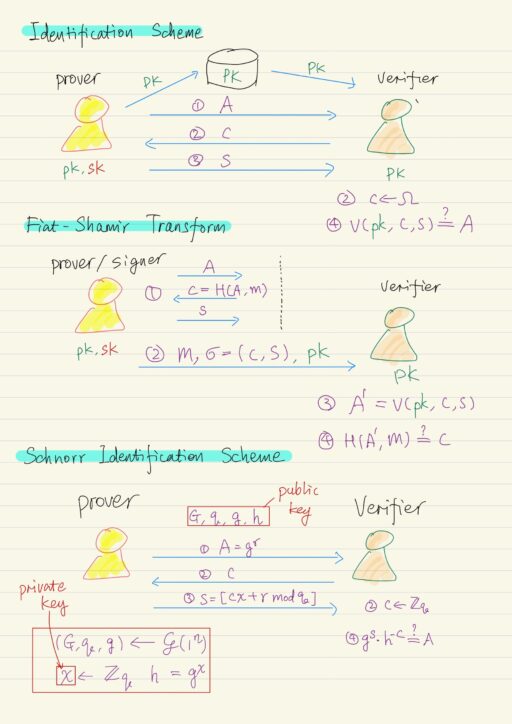
Identification Schemes Identification schemes are extremely important as building block for digital signature scheme. An identification scheme is a protocol that is running in the public key setting. There are two parties: prover and verifier. Prover Generates a pair of public and private keys.Publicize their public keys. Verifier Obtain authentic copy of the prover’s public…
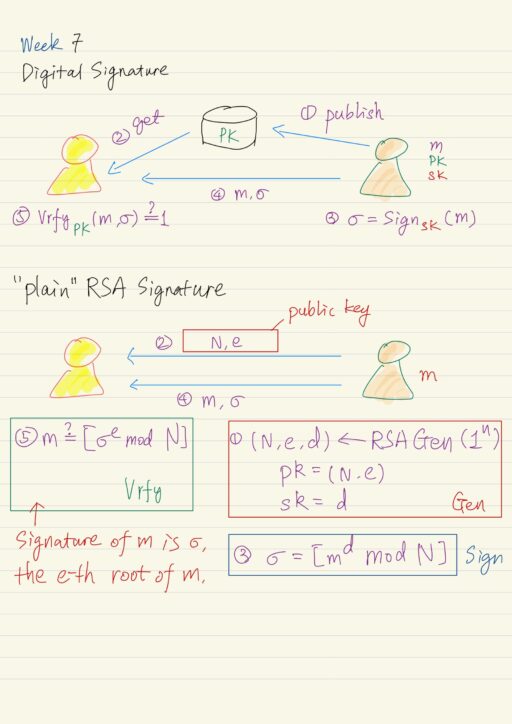
Digital Signature
Digital signature is a mechanism that can be used to provide integrity in the public key setting, analogous to message authentication codes in the private key setting. However there is some key differences between the both. How does digital signature work? Digital signature Public key encryption Sender Party has the private key Party has the…
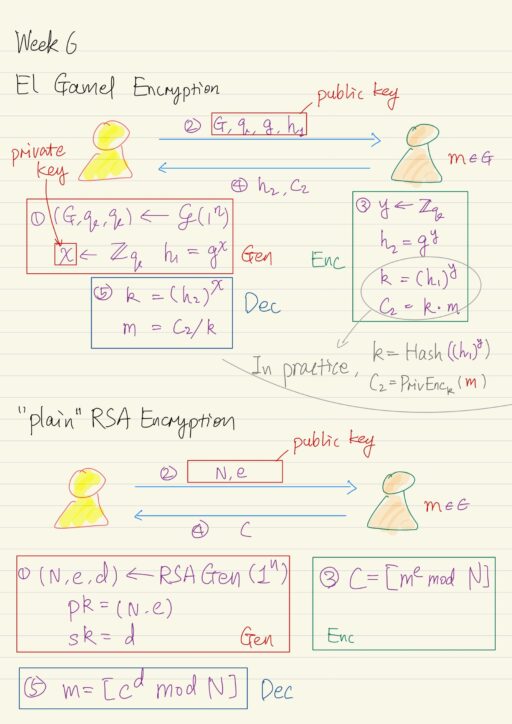
Public Key Encryption
A public-key encryption scheme is composed of three probabilistic polynomial time algorithms: Gen The key-generation algorithm that on input 1n (where n is security parameter), outputs public key pk, and private key sk. Enc Encryption algorithm that on input pk and a message m, outputs a cipher text c. Dec Decryption algorithm that on input…
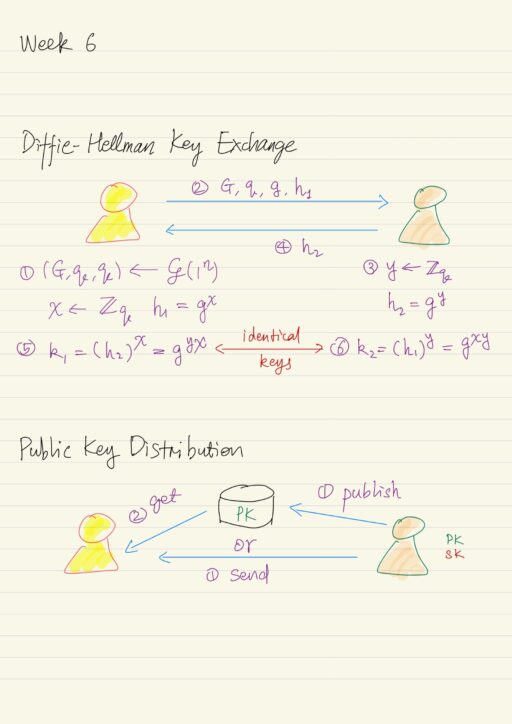
Public Key Revolution
A New Direction in Cryptography Recall that the private-key cryptography allows two users who share a secret to establish a “secure channel” which is a way to communicate with both secrecy and integrity. But the problem is that the need to share this secret key incurs several drawbacks. “Classical” private key cryptography offers no solution…
Factoring, RSA, Discrete-Logarithm and Diffie-Hellman
Problems like addition, multiplication, modular arithmetic, exponentiation can be solved in polynomial time, so they are seen as easy problem. Factoring a random number seems not hard, because 50% of the time, random number is even; 1/3 of the time, random number is divisible by 3. But the problem of factoring some special numbers can…
Number Theory and Group Theory
Number theory studies integers and operation on them. Basics of number theory have natural application, like addition, subtraction, etc. However advanced number theory topic has been praised as a branch of pure mathematics, mathematics for itself. This does not mean the number theory is useless. Things changed dramatically in computer era. … virtually every theorem…
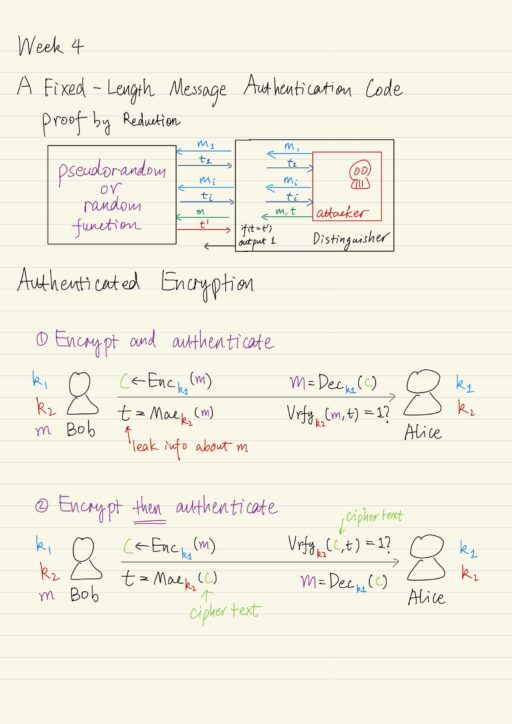
Message Authentication Codes & Authenticated Encryption
Besides the secrecy of communication, we also need to be concerned with integrity, which ensures that a message received by the receiver, originated from the intended sender, and was not modified, even if an attacker controls the channel. The standard error-correction techniques are not enough, because here we are not concerned with random errors, instead…
Private Key Encryption
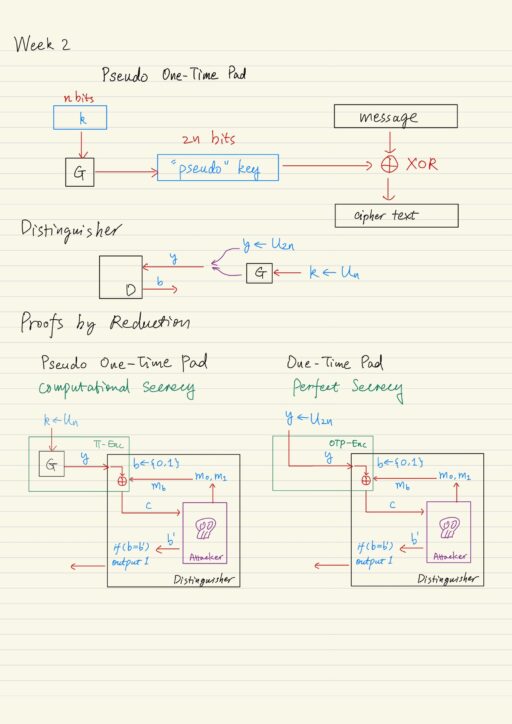
Limitations of Perfect Secrecy Recall that the perfect secrecy has two limitations: The first limitation can be circumvented by relaxing the notion of perfect secrecy to computational secrecy. In particular, the pseudo one time pad scheme allows parties to securely encrypt a very long message using a short key. In order to circumvent the second…
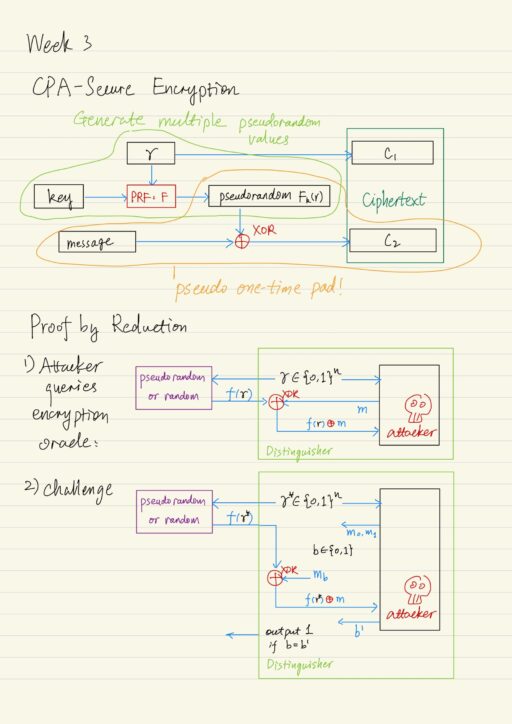
Computational Secrecy, Pseudo-randomness, and Proof of Security
Limitations of the One-Time Pad The one-time pad encryption scheme achieves perfect secrecy, but nowadays it is not often used because of several limitations: The key is as long as the message. Only secure if each key is used to encrypt a single message. Actually these limitations are not specific to the one-time pad scheme,…
Introduction to Classical Cryptography
In dictionary, cryptography is defined as the art of writing or solving codes. Historically, cryptography focused exclusively on codes (or private-key encryption schemes) ensuring secret communication between two parties who share secret in advance. Modern cryptography however has a much broader scope like data integrity, user authentication, protocols, etc. Furthermore cryptography also considers the public-key…