Quantum MechanicsUniversity of Colorado Boulder If you’re with mechanical or aerospace engineering backgrounds and looking for a course that presents an introduction to quantum mechanics, this course is right for you. The course covers the most fundamental concepts and plenty of stuff. I have to say the pace of this course is fast, you need…
Tag: Statistical Thermodynamics Specialization
Real Atoms and Molecules
Unfortunately, real atoms (including hydrogen atoms) are not very well described by the simple theory. There are more things contribute to the actual atomic structure: Higher order effects Spin-orbit coupling Relativistic Nuclear spin Zeman Identity particles, that leads to the Pauli exclusion principle. Multiple electrons, the electromagnetic fields associated with the electrons can interact. Spin-Orbit…
Hydrogenic Atom and Diatomic Molecule
External Motion Particle in a box is the simplest problem in quantum mechanics. A particle is just translating back and forth between the walls of the box. If there is no external field acting on the particle, i.e. no force acting on the particle except at the walls, then you can decompose the problem into…
Introduction to Quantum Mechanics
Quantum mechanics is the mathematics of atomic and molecular structure. We seek to determine allowed quantum states and their energies. A Short History A definite understanding that atoms are composed of separate particles (nuclei and electrons) did not really occur till toward the end of the 19th century. The development of quantum mechanics is strongly…
My #86 course certificate from Coursera
Fundamentals of Macroscopic and Microscopic ThermodynamicsUniversity of Colorado Boulder This is is course about physics. But why do you, as an IT practitioner, need to learn thermodynamics? If the notion of information still seems intangible, unreal, and ephemeral. This course probably will be the winds to howl, blowing away the spooky fog, because energy is…
Statistical Thermodynamics
Role of Statistics Statistics is the study of systems that exhibit variability. Because macroscopic systems are composed of atoms and molecules that are in constant motion, what we see at the macroscopic level are averages of that variability. Suppose we knew the kinetic energy of every molecule in a volume, then the average kinetic energy…
Macroscopic Thermodynamics
First of all, a quick introduction to 4 the most important figures in thermodynamics: Sadi Carnot (1796-1832) who discovered the second law of thermodynamics. Rudolf Clausius (1822-1888) who restated the Sadi Carnot’s principle into the form we use today. William Thomson (Lord Kelvin, 1824-1907) who brought thermodynamics into its modern form. Max Planck (1858-1947) who…
Thermodynamics: Fundamental Concepts
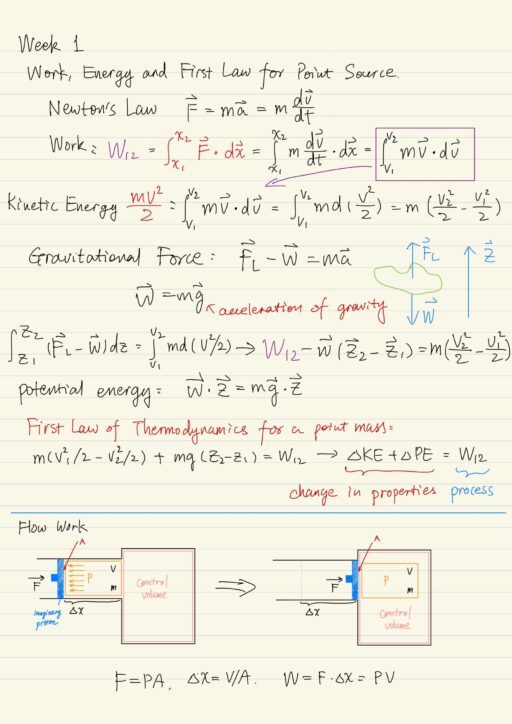
Thermodynamics is the study of the equilibrium behavior of systems, for which motion at the microscopic level of atom and molecules is important. It involves solving problems that arise because of work, heat transfer, mass transfer interactions with a working substance of some kind. Microscopic behavior determines macroscopic properties such as PVT relations, internal energy…