For hundreds years, space and time were absolute in the concept of Newton, they are something that can not be changed. Since a hundred years ago, we understood special relativity, space and time were put together – one object that can transform to each other. Further, we have general relativity that space and time are not only one object unified, but also it is dynamical – space and time can be affected by matter. This will give us a theoretical ground to the cosmology and quantum gravity.
Principle of Relativity
Galileo proposed the principle of relativity about 400 years ago. Put it ins a formal way: laws of nature take the same form in all inertial frames. There are different ways to put the Galileo’s principle of relativity as well:
- Motion is relative.
- Nobody is moving in absolute sense.
- Laws of nature is invariant under a boost (change of reference frame).
One of the best known examples that satisfies Galileo’s relativity is Newtonian mechanics.
Speed of Light
More than 300 years ago, Romer already knew that the speed of light is finite, by studying the eclipse of a moon of Jupiter. Modern experience shows the speed of light is c = 3 × 108 m/s . But the velocity addition law from Newtonian mechanics does not apply to light. When calculating the speed of light emitted from a running car with speed v, the Michelson-Morley experiment tells us that it is c, but Newton’s velocity addition law tells us that it is c + v. There is a contradiction between a theory and an experiment.
Einstein’s Postulates
- ℂ: The vacuum speed of light is a constant c for all inertial frames.
- ℝ: Galileo’s principle of relativity.
- ?: An event happened or not is independent of observers. Event is something happened at a small space volume (a point in space) and a particular moment (a point in time). In other words, an event is something happened at space-time point.
Light Clock
Absolute, true and mathematical time, of itself, and from its own nature, flows equably without regarding to anything external.
Newton
A simple way of defining time is to use the speed of light with a device called light clock, where td is the time the light is detected, te is the time the light is emitted, D is distance and c is the speed of light.
Unit of time ∆t = td - te = 2 * D / cTime Dilation
Suppose there are 2 people: A is in a car with a light clock inside the car, and the car is moving with velocity; B is standing on the ground. The observed duration of a unit time ∆t with respect to A and B are:
∆tA = ∆t
∆tB = ∆tA 1/√(1-v2/c2)In other words, for the same tick-tock event of a light clock, B sees a longer duration compared to A moving with the car. Bob is seeing that everything about Alice moving in the car slowed down. Time is no longer absolute.
Four-steps reasoning
- Physically define a device which can actually be measured, here the device will be the light clock, which can define the time duration in an operable way.
- Load the device onto people A’s car which is moving. A is not referring to outside, just looking at the device. According to A, nothing interesting will be happening because of the principle of relativity.
- People B stands on the ground, as a static observer. According to B, the light clock in particular slows down when A’s car is moving.
- One device stands for all possible devices.
Twin Paradox
Motion is relative. When A’s car is moving, B is actually also moving in the opposite direction. If B also carries a clock, A will also find B slows down. What we’re talking about is not actually the light wave that comes to our eyes to define time, but we are talking about a coordinate time. The coordinate time of A with respect to B slows down, and the coordinate time of B with respect to A slows down. There’s nothing wrong since now time becomes relative. Coordinate time for one person can be perfectly okay to be different from the coordinate time of another person.
After A has been leaving for a while and returned back to B, B will be older and A will be younger. Because there has to be a stage of acceleration when A is turning back. Then A is not always in an inertial frame, so our calculation, which applies to a inertia observer does not that always apply to A, but it always apply for B.
It is not special relativity can not deal with acceleration, special relativity perfectly can. What special relativity cannot deal with is the known laws of nature in a non-inertia reference frame.
Physical Picture
When facing modern physics, don’t gave up your intuition and physical picture. When you are looking problems, there are at least 3 ways of trying to solve the problem:
| Pattern matching | Try to match the problem with a problem that you are familiar with. However the framework of physical thinking is not really by similarities, but by first the principle reason. |
| Inverse search | Starting from what the question asked, then try to search the answer. |
| Physical intuition | Try to play a movie in our mind. Do not give up physical intuition even in the modern era of physics. Physical picture connects you to the real world. It will tell you in which way the solution that you’re working on makes sense. |
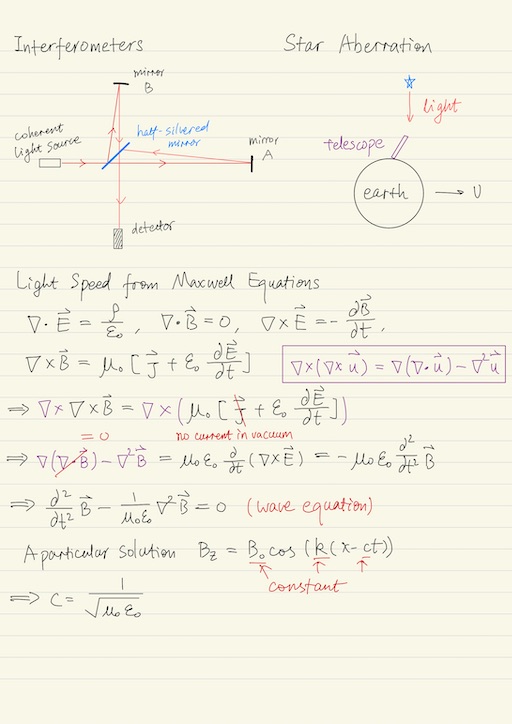
Interferometers
Michelson and Morley made an experiment to show that the speed of light is irrelevant to the direction of the motion of the earth.
… most of the grand underlying principles have been firmly established… the future of truth of physical science are to be looked for in sixth digit of decimals…
Michelson 1894
When he looks for the constants of nature in sixth digit of precision, he found something amazing to revolutionize the underlying principles of physics. What he did is nowadays known as interferometry. An interferometor is something with a coherent light source (a plain wave form of light), from which a beam of light is emitted. The beam of light goes through a half silvered mirror, i.e.
- half of the strength of the light beam passes through the mirror, reaches mirror A.
- another half of the strength of the light beam got reflected but reaches mirror B.
Both mirror A and B reflect their light beams, and both of the light beams go back to the half silvered mirror again, and eventually meet at the detector C. They may become:
| Constructive interference | Both of the waves are oscillating up, and there is a bigger amplitude of oscillating. |
| Destructive interference | One wave is oscillating up, the other is oscillating down, they cancel each other. You will see nothing on the detector. |
So, you will see fringes on the detector. The fringes give you the possibility to see the “sixth digit of decimals”, which is what Michelson wanted. The size of the experiment device is about 1 meter, however the wavelength of the light can be 10-6 meters. So this will simply give you the sixth digit of decimals” precision from such an optical experiment. The modern interferometer can be as precise as 10-21 meters. This was used to measure the speed of light and a lot of other things. For example, you can even do Fourier transformation using this device.
Ether
In history people believed that light travel via media named Ether, the reason is there are other kinds of waves which need media to travel, say, sound wave and water wave. For example if sound wave is traveling in wind with speed v m/s, then the sound speed will be (340 + v) m/s, because the sound is carried by the media.
However this is not the case for light, because electromagnetic waves can travel freely in vacuum. This can be proven by ruling out all possible situations, if we suppose that Ether exist:
- Situation 1: if the Ether does not move with the Earth, i.e. the Earth is traveling in the Ether which has relative motion with respect to the Earth.
- In this situation, Michelson and Morley experiments should have the result that light traveling in different directions has different speeds. This is in contradiction with the actual result of the Michelson-Morley experiment.
- Situation 2: if the Ether moves with the Earth.
- The starlight aberration experiment tells that we want to watch a star that is exactly on our head, we can not use telescope perpendicular to the earth to find the star. The correct way to find the star is to slightly lean the telescope to the direction of the motion of the earth. This tells us that Ether can not move with the Earth, if the Ether exists.
The Michelson-Morley experiment and the star aberration experiments together imply that the Ether should not exist at all and the light does not obey Newtonian mechanics. Light can freely travel in vacuum.
Speed of Light from Maxwell Equations
Michelson and Morley’s experiment has shown that the speed of light is independent of the emitter. But also it is a consequence from the Maxwell’s equations. From the Maxwell equations, we can derive the existence of light and there is a prediction about the speed of light.
c = 1/√(μ0ε0)In fact, special relativity is the hidden mathematical structure of the Maxwell equations. Maxwell at that time didn’t realize it.
The speed of light is exactly 299,792,458 m/s, actually this is the conversion between the definition of meter and the definition of second.
My Certificate
For more on Special Relativity: Space and Time, please refer to the wonderful course here https://www.coursera.org/learn/understanding-modern-physics-1-relativity-and-cosmology
Related Quick Recap
I am Kesler Zhu, thank you for visiting my website. Check out more course reviews at https://KZHU.ai