Fundamentals of Macroscopic and Microscopic ThermodynamicsUniversity of Colorado Boulder This is is course about physics. But why do you, as an IT practitioner, need to learn thermodynamics? If the notion of information still seems intangible, unreal, and ephemeral. This course probably will be the winds to howl, blowing away the spooky fog, because energy is…
Tag: Fundamentals of Macroscopic and Microscopic Thermodynamics
Statistical Thermodynamics
Role of Statistics Statistics is the study of systems that exhibit variability. Because macroscopic systems are composed of atoms and molecules that are in constant motion, what we see at the macroscopic level are averages of that variability. Suppose we knew the kinetic energy of every molecule in a volume, then the average kinetic energy…
Macroscopic Thermodynamics
First of all, a quick introduction to 4 the most important figures in thermodynamics: Sadi Carnot (1796-1832) who discovered the second law of thermodynamics. Rudolf Clausius (1822-1888) who restated the Sadi Carnot’s principle into the form we use today. William Thomson (Lord Kelvin, 1824-1907) who brought thermodynamics into its modern form. Max Planck (1858-1947) who…
Thermodynamics: Fundamental Concepts
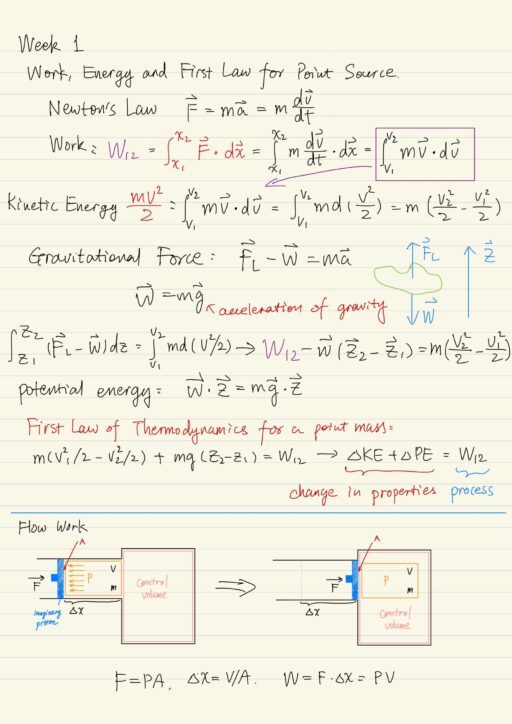
Thermodynamics is the study of the equilibrium behavior of systems, for which motion at the microscopic level of atom and molecules is important. It involves solving problems that arise because of work, heat transfer, mass transfer interactions with a working substance of some kind. Microscopic behavior determines macroscopic properties such as PVT relations, internal energy…