Financial Engineering and Risk Management Part IColumbia University An amazing course from a prestigious university! This course touches the hard core of various financial concepts by deriving numerous math equations. It effectively demonstrated why Financial Engineering is a multidisciplinary field drawing from economics, statistics, and engineering. It usually costs me a few hours to fully…
Tag: Financial Engineering and Risk Management Part I
Mortgage Backed Securities
Mortgage based securities are a particular kind of asset-based securities. They are asset-backed by underlying pools of securities like mortgage, auto / student loans, credit card receivable, and so on. The process by which asset-based or mortgage-based securities are created is called securitization. By securitizing, we enable the sharing and spreading of risk. There are…
Pricing Defaultable Bonds and Credit Default Swap
Defaultable Bonds A defaultable bond has these characters: We have to specify the probability of default by working directly with risk-neutral probability Q. We will model the term structure of default using 1-step default probability h(t). As with other fixed income securities, we are going to calibrate h(t) to market prices. We will need to…
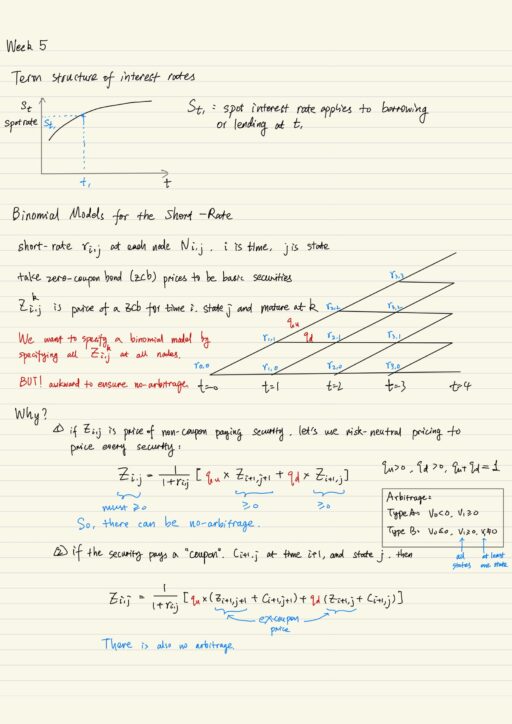
Financial Engineering: Term Structure Models
Fixed Income Derivatives Fixed income markets are enormous and in fact bigger than equity markets. Fixed income derivative markets are also enormous, including: Fixed income models are inherently more complex than security models, because it needs to model evolution of entire term-structure of interest rates. One of the classic ways to get around this problem…
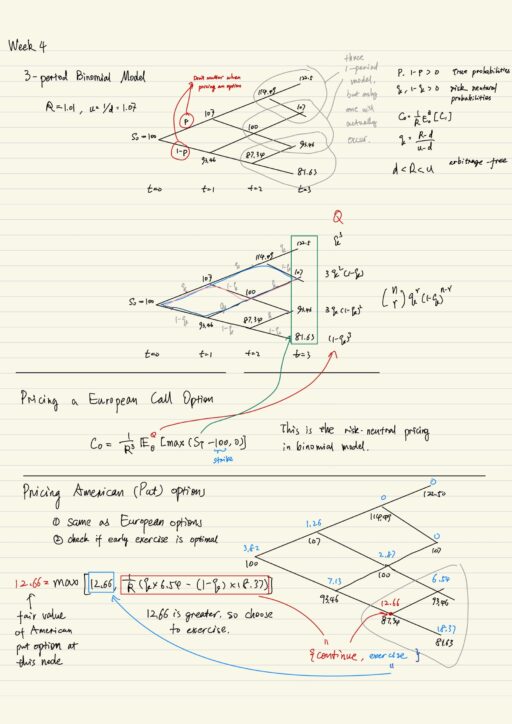
Multi-Period Binomial Model
Multi-period binomial model Multi-period binomial model is really just a series of one-period model spliced together. When pricing an European option, you can calculate it backward 1 period at a time. But you may also do the same thing just as one calculation. It appears the true probabilities p (price going up) and 1-p (price…
Derivative Securities: Swaps, Futures and Options
Swaps Why do companies or entities construct swaps? Because they want to change the nature of cash flows, or leverage strengths in different markets. But there is an implicit assumption that the companies / entities continue to exist. If one of them were to default, it will expose the counter party to a big risk….