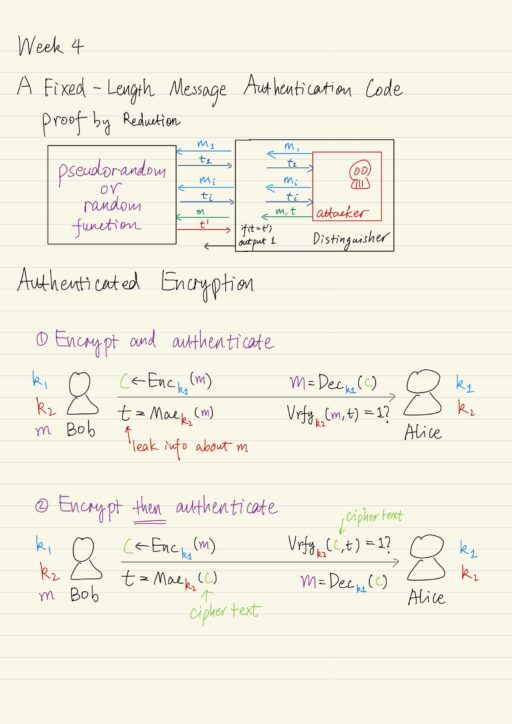
Besides the secrecy of communication, we also need to be concerned with integrity, which ensures that a message received by the receiver, originated from the intended sender, and was not modified, even if an attacker controls the channel. The standard error-correction techniques are not enough, because here we are not concerned with random errors, instead…
Google Docs at a Glance
Google Docs is Google’s online processor that is part of Google Workplace. You can create, view, and edit your Google Docs documents all with just a web browser. It’s also easy to share with anyone. It also works well with Microsoft Word files and many other formats. Go to https://docs.google.com to launch Google Docs and…
My #84 course certificate from Coursera
Physical Basics of Quantum ComputingSaint Petersburg State University It is challenging for lecturers to jam so much knowledge in one course, meanwhile equivalently challenging for learners to grasp the knowledge well. Don’t try this course until you have gotten a solid background in quantum mechanics. I have to admit the first week’s contents cost me…
Private Key Encryption
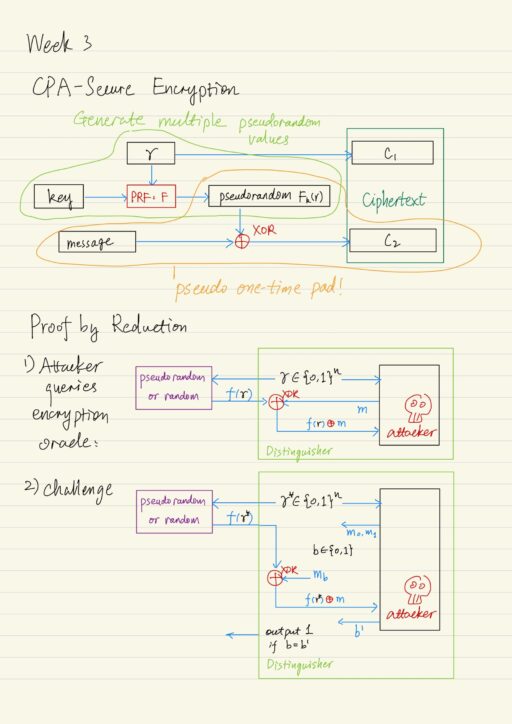
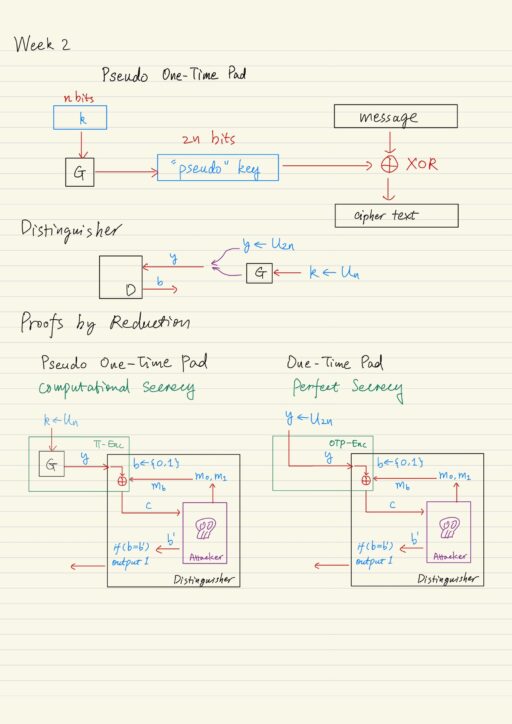
Limitations of Perfect Secrecy Recall that the perfect secrecy has two limitations: The first limitation can be circumvented by relaxing the notion of perfect secrecy to computational secrecy. In particular, the pseudo one time pad scheme allows parties to securely encrypt a very long message using a short key. In order to circumvent the second…
Thermodynamics: Fundamental Concepts
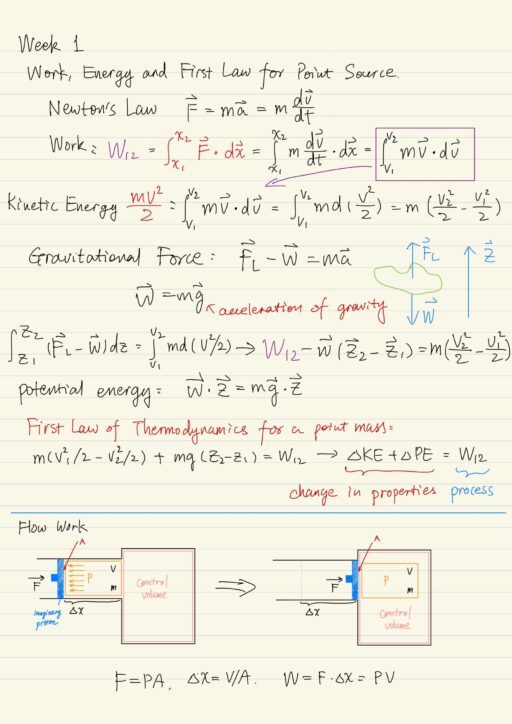
Thermodynamics is the study of the equilibrium behavior of systems, for which motion at the microscopic level of atom and molecules is important. It involves solving problems that arise because of work, heat transfer, mass transfer interactions with a working substance of some kind. Microscopic behavior determines macroscopic properties such as PVT relations, internal energy…
My #83 course certificate from Coursera
Foundations of Quantum MechanicsUniversity of Colorado Boulder This is a challenging course. If you are serious about learning quantum mechanics, I highly recommend this course to you. Furthermore if you want to engage yourself with quantum computing, this course is an excellent choice to lay the foundations. Your quest starts here: the time-independent Schrödinger equation…
Basics of Quantum Error Correction Theory
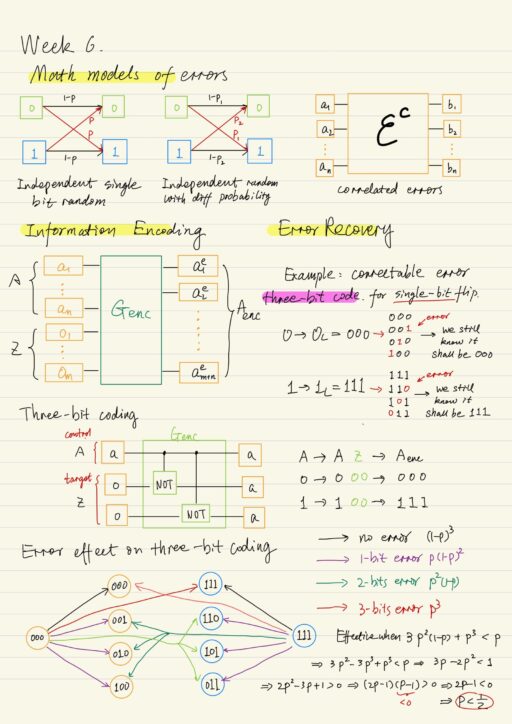
The real physical devices that implement computational models are always imperfect. It is not always possible to eliminate all of error sources in practice, however in many cases one could minimize the chances of their occurrence. Classical Error Correction Theory There are three main problems in classical error correction theory: Information channel is an important…
Quantum Algorithms
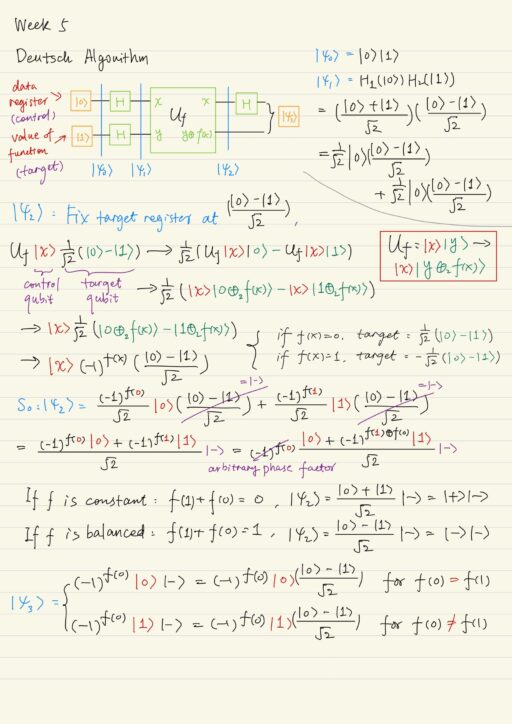
The essence of the quantum computations might not determine some particular result for a certain function, but establish the global properties of this function. For example, in the Deutsch problem, we don’t find the individual values of a function, but consider the whole superposition of the values and make conclusions about whether the function is…
Transmission of Quantum Information
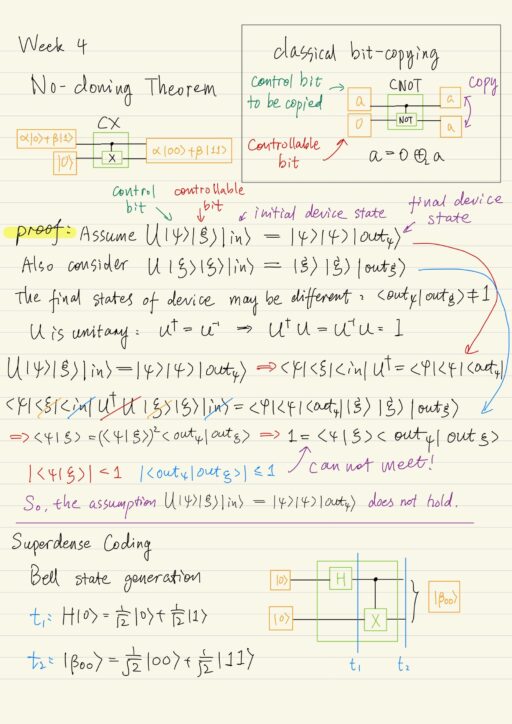
Unlike the classical bit, as we already know the quantum bit is able to stay in superposition state. When measuring a qubit in superposition state, one obtains every basis state with a certain probability. The probabilistic behavior of quantum objects has its effect on the logical operations. No-cloning Theorem Classical element FANOUT (bit-copying) could be…
Computational Secrecy, Pseudo-randomness, and Proof of Security
Limitations of the One-Time Pad The one-time pad encryption scheme achieves perfect secrecy, but nowadays it is not often used because of several limitations: The key is as long as the message. Only secure if each key is used to encrypt a single message. Actually these limitations are not specific to the one-time pad scheme,…
Quantum vs. Classical Logical Operations
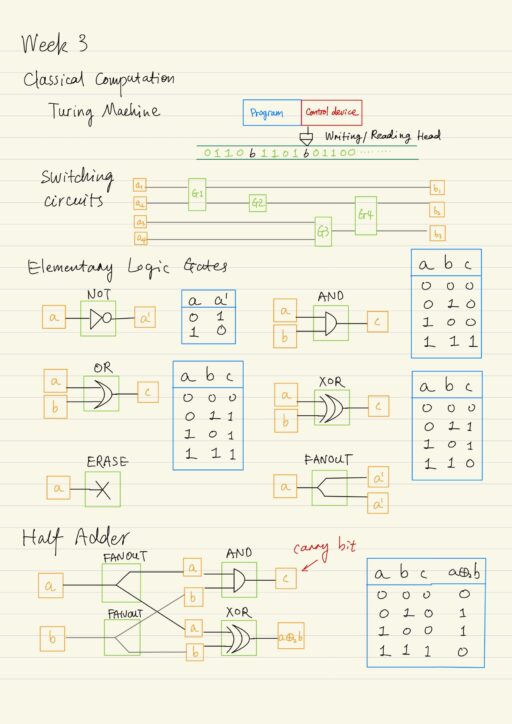
Nowadays, there are a large number of various computers. Despite the differences in physical implementations and the purposes of these devices, from the point of view on the computation theory, the operation principle of any of them can be described by Turing “machine”, which is formally called Church-Turing thesis. The main feature and advantage of…
Quantum Entanglement
Quantum entanglement acts as a cornerstone for all quantum computations. If one physical system consists of two or more qubits and its state vector |ζ⟩ can be represented as tensor product |ζ⟩ = |ζ1⟩ ⨂ |ζ2⟩, where |ζ1⟩ and |ζ2⟩ describe states of each qubit. Then the state |ζ⟩ is called separable; otherwise it is…
Introduction to Classical Cryptography
In dictionary, cryptography is defined as the art of writing or solving codes. Historically, cryptography focused exclusively on codes (or private-key encryption schemes) ensuring secret communication between two parties who share secret in advance. Modern cryptography however has a much broader scope like data integrity, user authentication, protocols, etc. Furthermore cryptography also considers the public-key…
Statistical Aspects of Quantum Mechanics
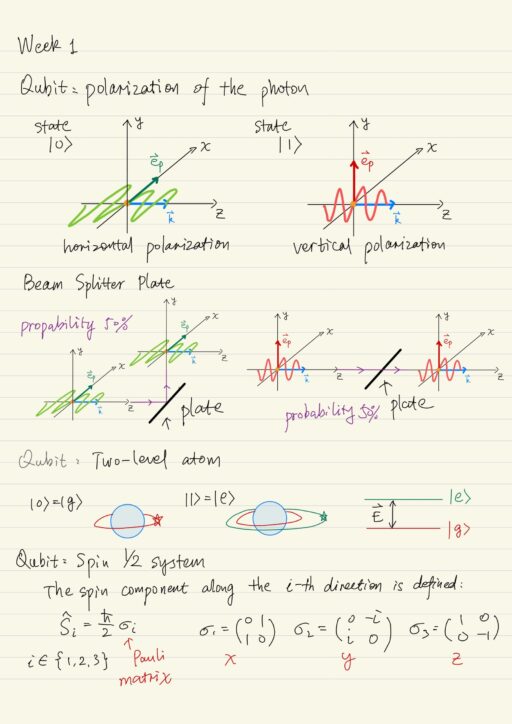
As of now, it is still unclear whether it is possible to create a so-called quantum computer, a special device which will be able to perform a special set of algorithms on the application of quantum mechanical effects. Qubit Implementation A qubit is the smallest element for storing and processing information in a quantum computer….
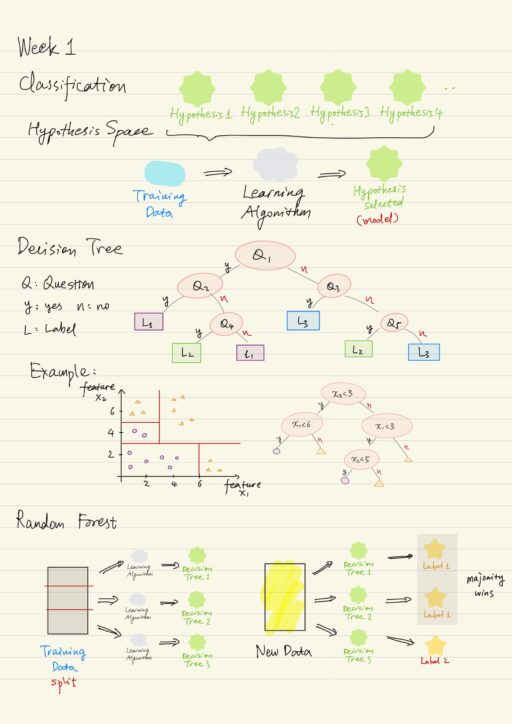
Classification: Decision Trees and k-Nearest Neighbours
Classification Basics Machine learning uses learning data and learning algorithms to produce a model (or Question Answering Machine, QuAM), which is used to make prediction on unseen data. Classifier is a specific kind of model, which is built by using the supervised learning technique called classification. Scientific method could be broken down into several steps:…