Pure and Mixed Ensemble / State In quantum mechanics, we only talk about average or expectation value for a physically observable quantity by taking multiple measurements on ensemble and taking average. Ensemble means a collection of identically prepared physical system. The Stern-Gerlach experiment is an example of producing an ensemble – a collection of electrons…
Time Evolution of Quantum States
Time-dependent Schrödinger Equation Time-dependent Schrödinger equations is not an eigenvalue equation, but allowing us to predict the state at t, given the initial condition at t0. where Hamiltonian H^ = -h2/2m ∇2 + V(x, t). The potential energy V(x, t) in general depends on time, however time-independent potential V(x) covers a large number of important…
My #82 course certificate from Coursera
Operations Research (2): Optimization AlgorithmsNational Taiwan University You probably have used some solver / optimizer software to solve problems, this wonderful course will show you what is under the hood. Being able to comprehend what has happened is crucial to customize the algorithms or even to develop your own ones. There is a warm-up at…
Quantum Mechanics: Uncertainty Principle and Change of Basis
Commuting Operators Two observables A and B are considered ‘compatible’ if the corresponding operators commute with each other, i.e.: [A^, B^] = 0, where [ ] is commutator bracket, and A^, B^ are operators representing the physical observables A and B. Commuting operators have two very important properties: Commuting operators share the same set of…
Heuristic Algorithms: A Case Study
The objectives for any research is that we want to build a mathematical model to formulate the given problem. The heart of operations research is a mathematical model. That model is going to precisely describe the problem, but the model may be too complicated to get an optimal solution. We need heuristic algorithms, and the model could be…
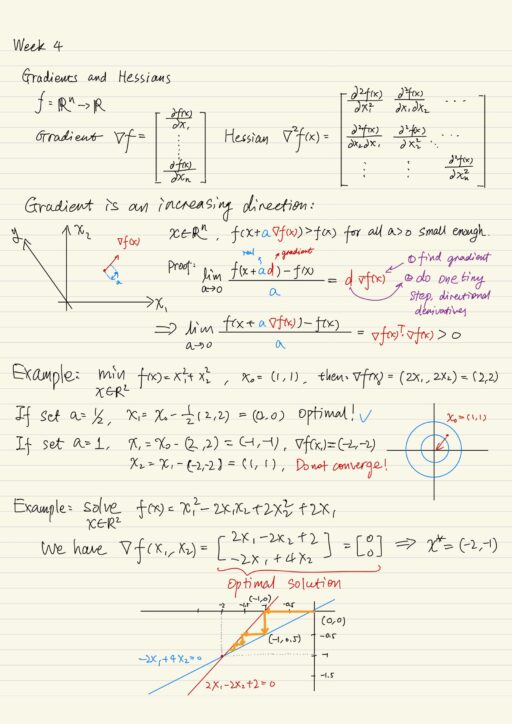
Non-Linear Programming: Gradient Descent and Newton’s Method
Non-Linear Programs When visualizing a linear program, its feasible region looks like a polygon. Because the objective function is also linear, the optimal solution is on the boundary or corner of the region. But a non-linear program is quite different, its feasible region may be in any shape, moreover the optimal solution may not exist…
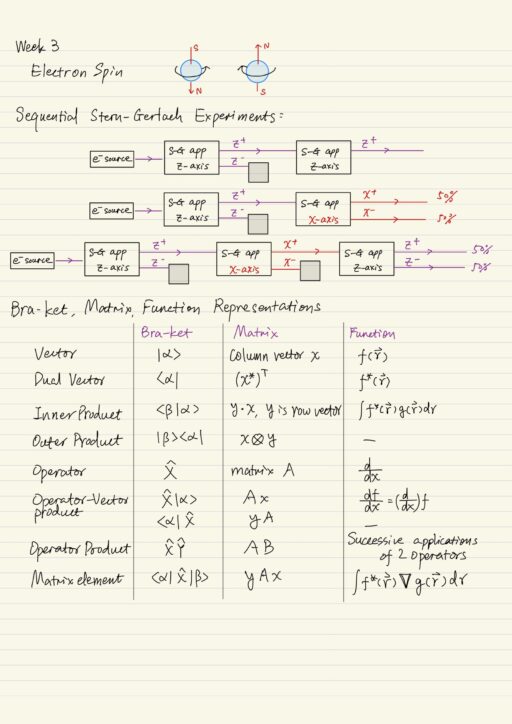
Stern-Gerlach Experiments & Dirac Bra-ket Notation
Electron Spin Electron has intrinsic angular momentum called spin that is not associated with its orbital motion. And just like orbital angular momentum, spin angular momentum produces magnetic moment. Therefore electrons interact with magnetic field through both orbital and spin angular momentum. The electron is not actually spinning, electron produces angular momentum as if it…
My #81 course certificate from Coursera
Vector Calculus for Engineers The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology We can’t emphasize enough the importance of Vector Calculus. A solid understanding lays the foundations for further learning of electromagnetism, fluid mechanics and many disciplines. This course is one of the best I have met. I can’t help but recommend to those who…
Special Relativity: Space and Time
For hundreds years, space and time were absolute in the concept of Newton, they are something that can not be changed. Since a hundred years ago, we understood special relativity, space and time were put together – one object that can transform to each other. Further, we have general relativity that space and time are not…
Quantum Mechanics: 1-Dimensional Finite Potential Problems
Finite Potential Well Finite potential well problem is more realistic compared to the infinite potential well. It is specified by this potential profile V(z). If the energy of the electron E is greater than the well depth V0, the electron can escape the potential well and then can free to move around. The case where…
Time-Independent Schrödinger Equation
Wave-particle Duality The double-slit experiments show us: particle source P1 : probability pattern when slit 1 is openP2 : probability pattern when slit 2 is openP12 = P1 + P2 : probability when both slits are open wave source (intensity of wave I is defined by its amplitude a)I1 = |a1|2 : when slit 1…
My #80 course certificate from Coursera
Differential Equations for EngineersThe Hong Kong University of Science and Technology By highlighting both theories and applications in practice, this amazing course might be your excellent choice to grasp the differential equations in shortest time. You are actually learning math and physics at the same time, building your own mapping between the 2 disciplines. I…
Vector Calculus: Fundamental Theorems
Gradient Theorem The fundamental theorem of single variable calculus was the one that told you “the integral of the derivative of a function is just going to be the function itself.” The gradient theorem is a generalization of the fundamental theorem of calculus to vector calculus, i.e. calculus of several variables. Suppose a scalar field φ, we could use…
Line and Surface Integrals
Line Integrals Scalar Fields We have a curve C in the x-y plane, we can represent a point on this curve then by a vector r. To do a line integral, we break the curve into small pieces ds, you have a small element of length ds and a value of f on that element, we multiply…
My #79 course certificate from Coursera
Logic for EconomistsUniversity of Amsterdam The logo of University of Amsterdam is cool, so is this succinct course. In this course you only experience black board, white chalk and the hushed tone of the professor. No distraction, you just focus on the “logic”! The course covers a few of the most basic concepts, they are…