Vector Calculus for Engineers The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology We can’t emphasize enough the importance of Vector Calculus. A solid understanding lays the foundations for further learning of electromagnetism, fluid mechanics and many disciplines. This course is one of the best I have met. I can’t help but recommend to those who…
Tag: Vector Calculus for Engineers
Vector Calculus: Fundamental Theorems
Gradient Theorem The fundamental theorem of single variable calculus was the one that told you “the integral of the derivative of a function is just going to be the function itself.” The gradient theorem is a generalization of the fundamental theorem of calculus to vector calculus, i.e. calculus of several variables. Suppose a scalar field φ, we could use…
Line and Surface Integrals
Line Integrals Scalar Fields We have a curve C in the x-y plane, we can represent a point on this curve then by a vector r. To do a line integral, we break the curve into small pieces ds, you have a small element of length ds and a value of f on that element, we multiply…
Polar, Cylindrical, Spherical Coordinates
Multidimensional Integration In Vector Calculus, we have to worry about integrating over two or three variables: double integrals or triple integrals. Double integral can be interpreted as a volume, like a single integral is the area under the curve. When the limits don’t depend on any variable, and we could do integrals separately. Polar coordinates Polar coordinates…
From Partial Derivatives to Maxwell’s Equations
Partial derivatives Partial derivative is to differentiate functions of multiple variables. Assume a function f = f(x, y), you are differentiating f with respect x, that is the usual definition of a derivative of a function of one variable, but y is held constant. There is something called mix partial. It does not depend on…
Vector Calculus: Basics
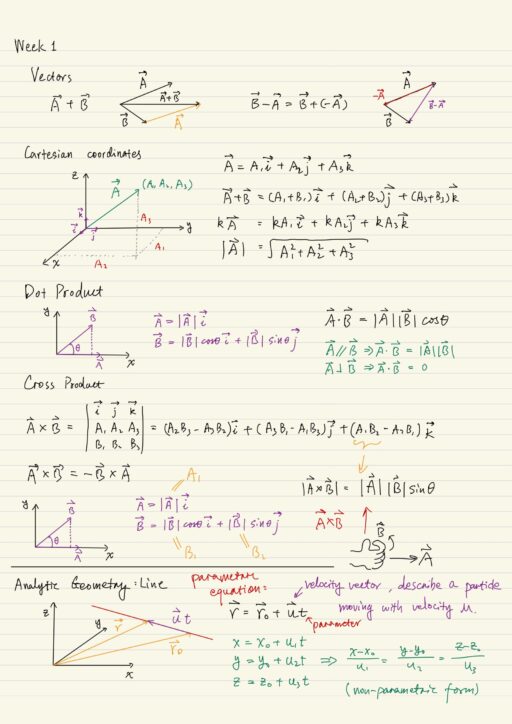
Vector Calculus is also known as Multivariate Calculus or “Calculus 3”. Calculus 1 and 2 are Differential Calculus and Integral Calculus respectively (both are single variate). Vectors A vector is a quantity that has a length associated with it, and a direction. It is not anchored in any particular spot. Besides, scalars are quantities that…