Machine Learning Algorithms: Supervised Learning Tip to TailAlberta Machine Intelligence Institute There are many other courses that teach you some aspects of supervised learning, but this one gives you the big picture. Classification and Regression are closely related, it’s likely to get lost in the details. The course begins with the Decision Trees and k-Nearest…
Category: Machine Learning
Regression and Classification Model Assessment
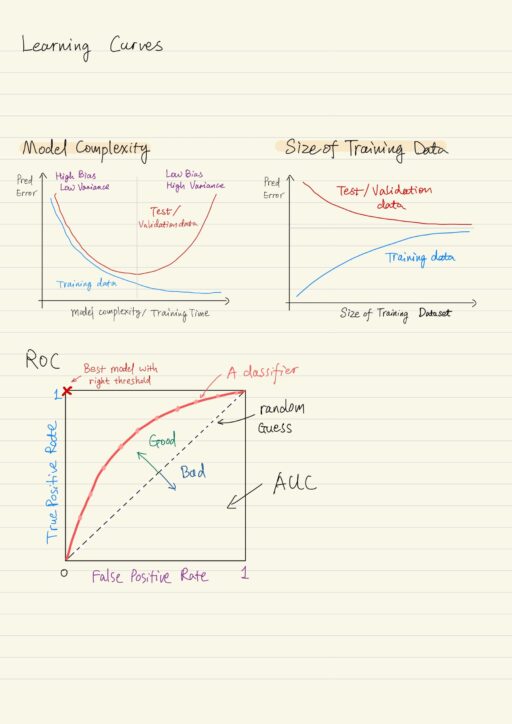
Let’s take a look at how the performance of regression and classification models can be quantified so that we can identify the best learning algorithm to build the model. Most importantly, the learning data should be split into training data and test dtaa. Failing to hold out test data will lead to dire consequences. Regression…
Logistic Regression & Support Vector Machines
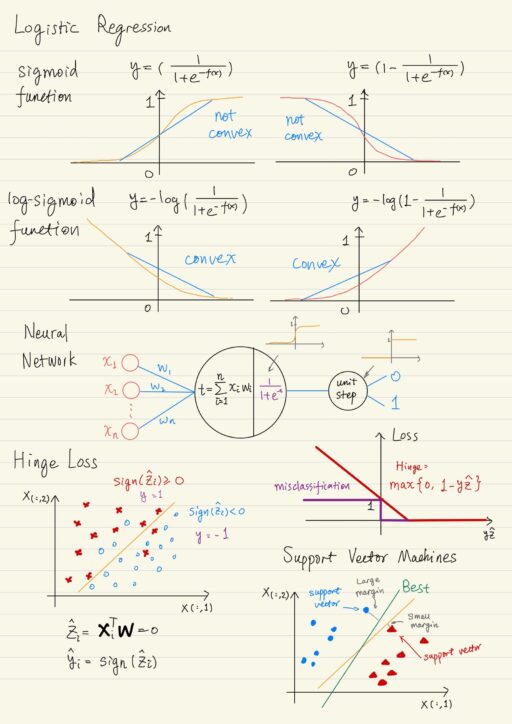
Often, some of the “shifts” we need to make when we’re using regression based approaches for classification. There is a major family of classification algorithms called Logistic Regression. Logistic Regression Logistic regression is actually a classification, it does not answer questions with a real number, it answers with a binary category 0 or 1. It…
Linear Regression
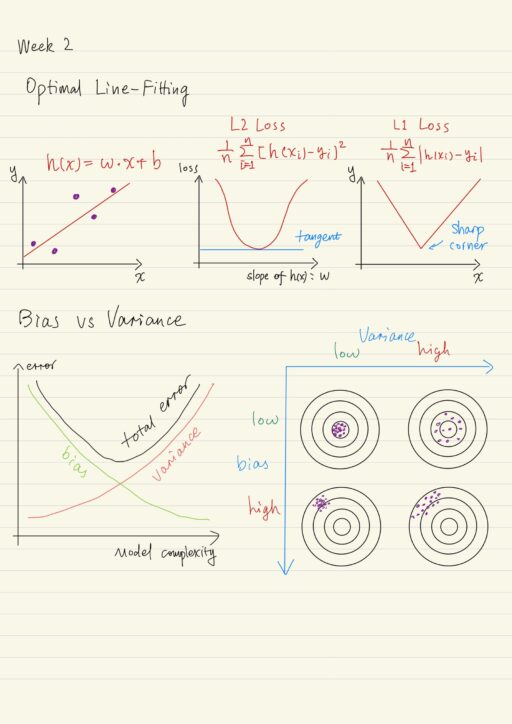
Recall that the concept of hypothesis spaces is a collection of hypotheses that might answer a particular question, and learning algorithms find the best hypothesis in the space of functions which we’ll call the model or QuAM. Previously we learned that classification learning algorithms operate in the space of functions that classify examples. However we can also think…
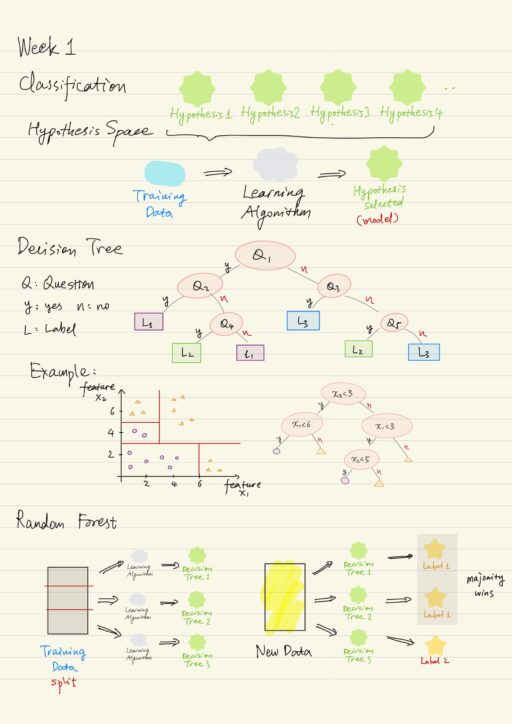
Classification: Decision Trees and k-Nearest Neighbours
Classification Basics Machine learning uses learning data and learning algorithms to produce a model (or Question Answering Machine, QuAM), which is used to make prediction on unseen data. Classifier is a specific kind of model, which is built by using the supervised learning technique called classification. Scientific method could be broken down into several steps:…
My #67 course certificate from Coursera
Getting started with TensorFlow 2Imperial College London Wow this is a wonderful course on Tensorflow! The professor and lecturers directly teach how to write code to complete certain tasks, piece-by-piece and step-by-step. Upon the moment of completing all programming assignments you would certainly gain Tensorflow skills and be confident in your next real job. You’d…
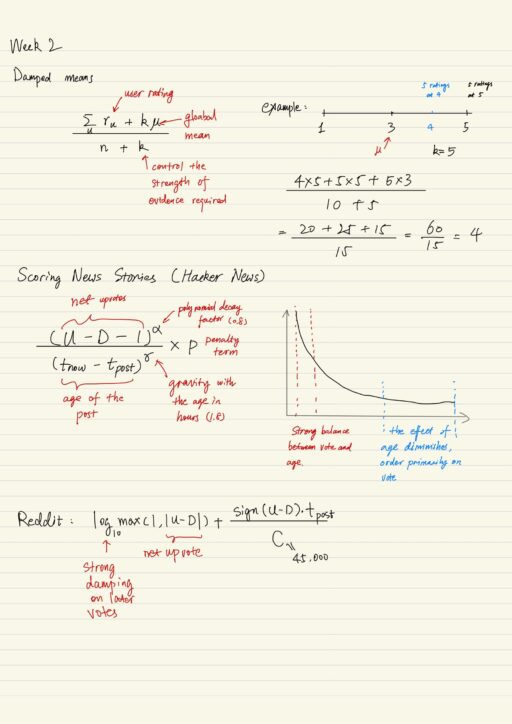
Non-personalized Recommenders
Non-personalized recommenders systems are remarkably effective tools and still useful in various situations. For example: recommendation in print for restaurants. Sometimes we know a little about users: age, gender, zip code. We can do a little week personalization. Also product associations allow recommendations based on current page, item, or context. Summary Statistics This is a…
Introducing Recommender Systems
Information Retrieval and Filtering Information retrieval evolved in response to the need to be able to ask questions about a large collection of documents. We have a static content base, and there is dynamic information need (a query). So we spend our time and invest in indexing the content base. The common approach used is…
My #61 course certificate (with Honors) from Coursera
Practical Reinforcement LearningHigher School of Economics I am very proud that I survived and completed this thorny but exciting journey with Honors. I spent nearly 1 month on this very challenging course, which covers enormous amount of knowledge. The lecture videos are all well-prepared, they not only help me consolidate my original understanding, but also…
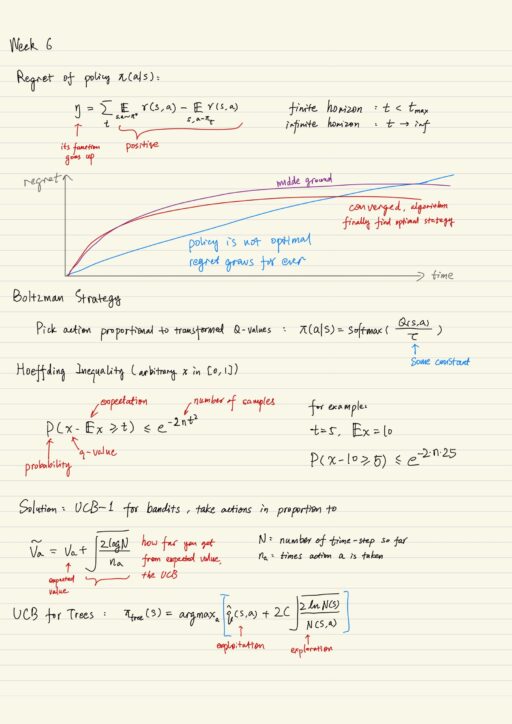
Exploration and Planning in Reinforcement Learning
Exploration is needed to find unknown actions which lead to very large rewards. Most of the reinforcement learning algorithms share one problem: they learn by trying different actions and seeing which works better. We can use a few made-up heuristics (e.g. epsilon-greedy exploration) to mitigate the problem and speed up the learning process. Multi-armed bandits…
Reinforcement Learning: Policy Gradient Methods
The problems of value-based methods The idea behind value-based reinforcement learning (say, Q-learning) is to find an optimal action, in a state, based on how much discounted reward you will get, by following a policy. The first problem here is value-based methods do not explicit learn “what to do”, instead it learns “what kind of…
My #60 course certificate from Coursera
Introduction to TensorFlowGoogle Quite a lot stuff of TensorFlow was distilled into this course, from the basics to advanced techniques. I guess some topics probably will make beginners confused, but will strike a chord with experienced developers. The course first introduced the layers of API, the very basic tensor and Variable. Then put much effort…
TensorFlow Essentials
TensorFlow is an open-source, high-performance library for any numerical computation (not just for machine learning). For example, you could use TensorFlow to solve partial differential equations. In order to make TensorFlow work, you need to create directed graph, which represent the computation you want to do. In a graph, nodes represent mathematical operations, edges represent…
My #58 course certificate from Coursera
Exploratory Data Analysis with MATLABMathWorks Even though Python, R and others are getting more and more popular, MATLAB is still irreplaceable and indispensable in some fields. If you are willing to refresh your MATLAB skill set, don’t miss this official course from MathWorks. It is quite easy to sign up an MathWorks account, get a…
My #57 course certificate from Coursera
How Google does Machine LearningGoogle Cloud There is no math, no Tensorflow, no algorithms in this short course – don’t be upset. It shared a lot valuable stuff : the enterprise know-how that Google have obtained over the years. I think In week 2 the lecture is rather wonderful and inspiring! The topics include the…