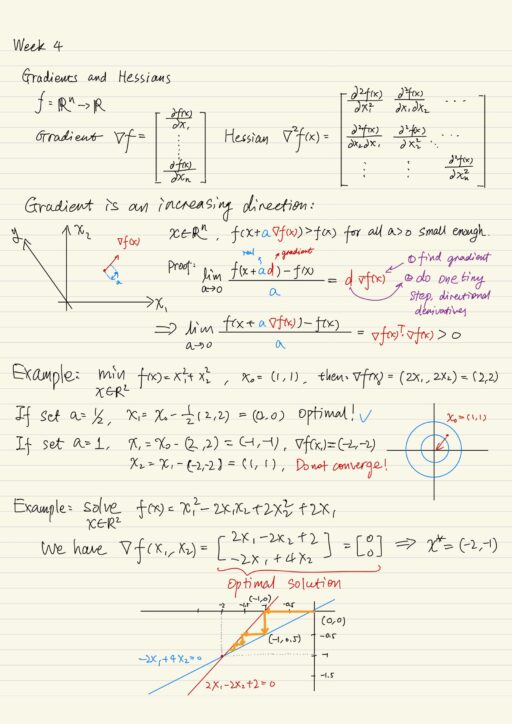
Non-Linear Programs When visualizing a linear program, its feasible region looks like a polygon. Because the objective function is also linear, the optimal solution is on the boundary or corner of the region. But a non-linear program is quite different, its feasible region may be in any shape, moreover the optimal solution may not exist…
Category: Quick Recap
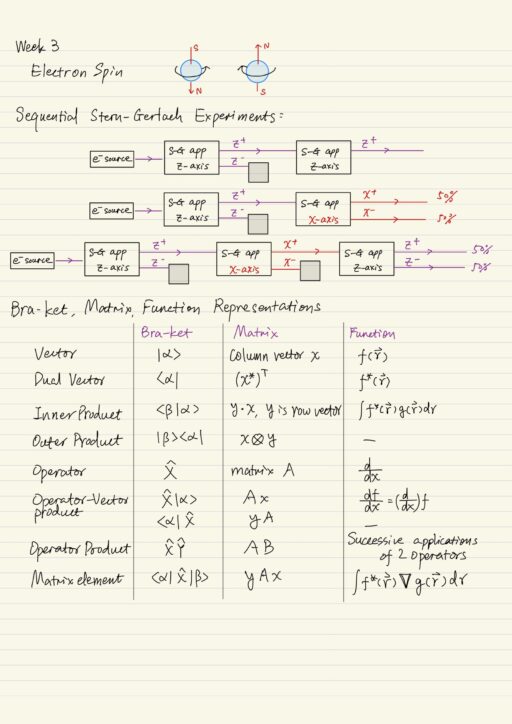
Stern-Gerlach Experiments & Dirac Bra-ket Notation
Electron Spin Electron has intrinsic angular momentum called spin that is not associated with its orbital motion. And just like orbital angular momentum, spin angular momentum produces magnetic moment. Therefore electrons interact with magnetic field through both orbital and spin angular momentum. The electron is not actually spinning, electron produces angular momentum as if it…
Special Relativity: Space and Time
For hundreds years, space and time were absolute in the concept of Newton, they are something that can not be changed. Since a hundred years ago, we understood special relativity, space and time were put together – one object that can transform to each other. Further, we have general relativity that space and time are not…
Quantum Mechanics: 1-Dimensional Finite Potential Problems
Finite Potential Well Finite potential well problem is more realistic compared to the infinite potential well. It is specified by this potential profile V(z). If the energy of the electron E is greater than the well depth V0, the electron can escape the potential well and then can free to move around. The case where…
Time-Independent Schrödinger Equation
Wave-particle Duality The double-slit experiments show us: particle source P1 : probability pattern when slit 1 is openP2 : probability pattern when slit 2 is openP12 = P1 + P2 : probability when both slits are open wave source (intensity of wave I is defined by its amplitude a)I1 = |a1|2 : when slit 1…
Vector Calculus: Fundamental Theorems
Gradient Theorem The fundamental theorem of single variable calculus was the one that told you “the integral of the derivative of a function is just going to be the function itself.” The gradient theorem is a generalization of the fundamental theorem of calculus to vector calculus, i.e. calculus of several variables. Suppose a scalar field φ, we could use…
Line and Surface Integrals
Line Integrals Scalar Fields We have a curve C in the x-y plane, we can represent a point on this curve then by a vector r. To do a line integral, we break the curve into small pieces ds, you have a small element of length ds and a value of f on that element, we multiply…
The Diffusion Equation of a Dye
Fourier Series Sometimes complicated motions can actually be composed of motions of many different frequencies. The type of mathematical analysis that’s useful is called Fourier series. Fourier series is a way of representing a function – an infinite series of cosine and sines. You can view these as a linear superposition of waves of various frequencies. We use orthogonality…
Systems of Differential Equations
Systems of Homogeneous Linear First-order ODEs The system of linear first order homogeneous equations can be written in matrix form. To solve it we’re going to use An ansatz X(t) = V eλt . We’re going to look for solutions of the ansatz. The principle of superposition. When we find solutions of the ansatz, we’ll multiply…
Polar, Cylindrical, Spherical Coordinates
Multidimensional Integration In Vector Calculus, we have to worry about integrating over two or three variables: double integrals or triple integrals. Double integral can be interpreted as a volume, like a single integral is the area under the curve. When the limits don’t depend on any variable, and we could do integrals separately. Polar coordinates Polar coordinates…
Branch-and-Bound & Heuristic Algorithms
In some cases, variables must take integer values, or binary values. Formulating and solving the models with integer variables is integer programming. There are mainly 2 methods to solve it: The branch-and-bound algorithm finds an optimal solution for an integer program. Essentially, it decomposes the integer program into multiple linear programs, then solves all of…
Laplace Transform and Series Solution Method
Laplace transform Laplace transform is a technique for solving differential equations. By using the Laplace transform you can convert a differential equation into another space where the equation is easier to solve. Laplace transform is a linear transformation and it is invertible. The strength of the Laplace transform technique, is to solve the differential equations where you…
From Partial Derivatives to Maxwell’s Equations
Partial derivatives Partial derivative is to differentiate functions of multiple variables. Assume a function f = f(x, y), you are differentiating f with respect x, that is the usual definition of a derivative of a function of one variable, but y is held constant. There is something called mix partial. It does not depend on…
Logic for Economists
Propositional Logic A proposition (often denoted by capital letters P, Q, etc) is a statement, that can be either true or false. Its negation ¬P is obtained by prepending “it is not true that …” to P. If you negate twice, you get P back again: ¬(¬P) = P . Two propositions are equivalent P…
Inhomogeneous Linear Differential Equations
The general form of inhomogenous linear differential equations is: We need 2 initial conditions x(0) = x0, x'(0) = u0 to have a unique solution, there is a 3-step method to solve it: Solve the homogeneous equation, where g(t) = 0, to find the general solution to the homogeneous equation:xh(t) = C1 x1(t) + C2…